The Core of Crypto Blockchain Technology Explained Simply
Blockchain sounds complicated, but it's simply a secure, shared, digital ledger. We break down the core concepts of blocks, chains, and decentralization to explain how this revolutionary technology works and why it matters for crypto and beyond
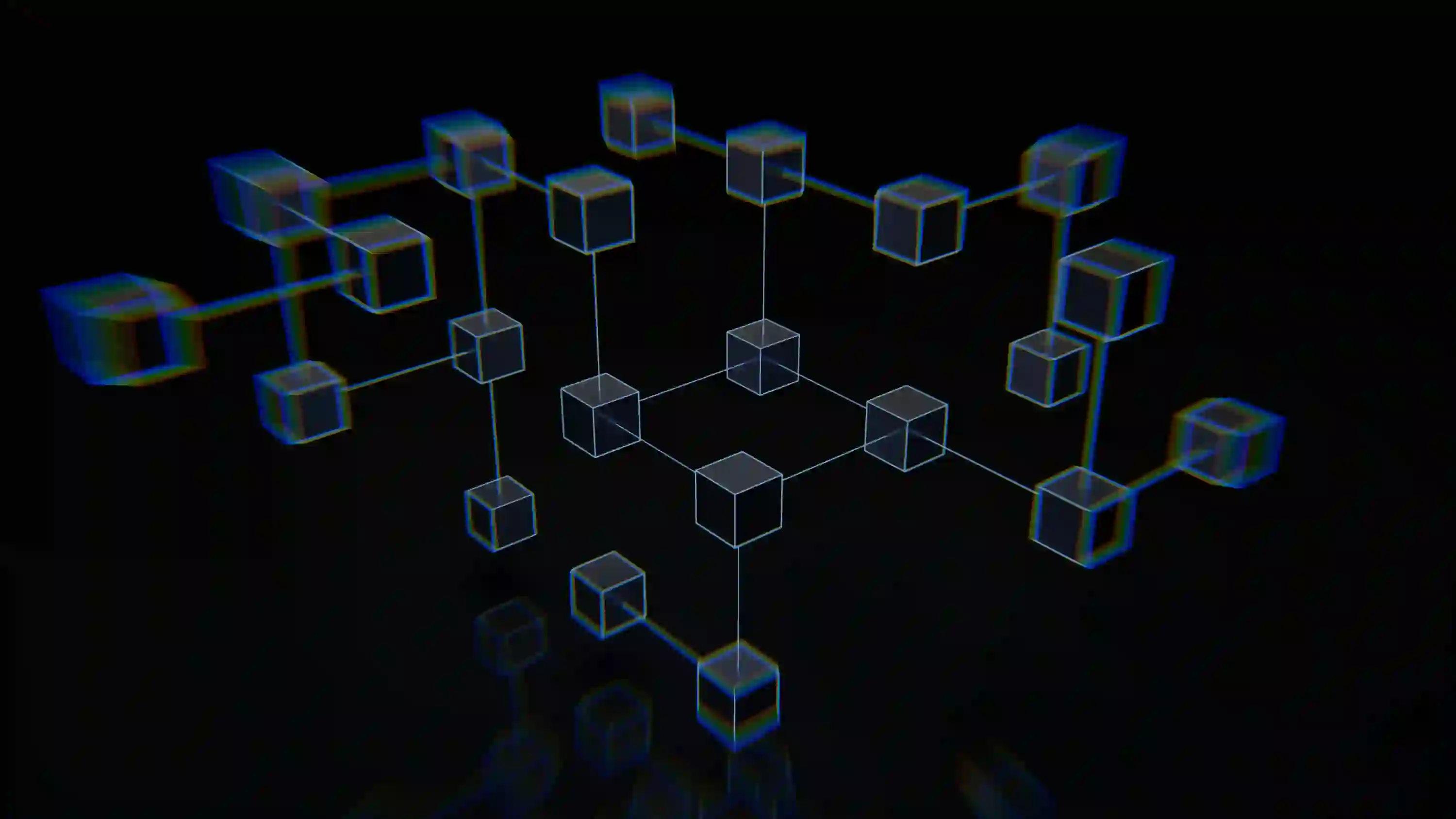
Blockchain technology sounds complex—a futuristic concept reserved for tech experts. However, at its core, the system is fundamentally simple. It is a distributed, digital ledger that records transactions and other data in a way that is secure, transparent, and almost impossible to change.
Understanding the blockchain is essential, as it forms the foundation of cryptocurrencies and the future of digital finance. This guide aims to demystify this technology by clearly breaking it down into its three simplest, most vital concepts.
Blockchain as a Shared Google Doc
To fully grasp blockchain, it helps to compare it to a traditional central database, such as the records maintained by a bank. In that conventional system, the bank alone is responsible for controlling, verifying, and securing all information.
A blockchain operates differently. Think of it as a Google Document that is shared with thousands of people globally.
- Traditional Database: A single person controls the master copy.
- Blockchain: The ledger is copied and simultaneously verified by every person (or computer) in the network. If anyone tries to change one copy, the other thousands of copies immediately prove it is invalid. This system is the foundation of its security.
The Three Core Concepts
The entire technology can be broken down into three main components: Blocks, Chains, and Decentralization.
Concept 1: The Blocks (Verified Transactions)
A "block" is simply a record of verified data—like one completed page in a ledger book. In the context of Bitcoin, a block contains a bundle of recent transactions (e.g., "Person A sent 1 Bitcoin to Person B").
- Once a block is filled with data, it is sealed using a unique cryptographic code called a "hash." This code acts like a highly complex digital fingerprint.
- This sealing process is what the computers in the network—known as "miners" or "validators"—must verify by solving a difficult math problem.
Concept 2: The Chain (Permanent Record)
Once a block is verified and sealed, it is linked chronologically to the block that came immediately before it.
- This creates a permanent, linear sequence: the Chain.
- Because each new block contains the unique cryptographic code (hash) of the previous block, changing data in any old block would immediately break the links in every block that follows it. This is why the data on a blockchain is considered tamper-proof.
Concept 3: Decentralization (No Single Authority)
Decentralization is arguably the most revolutionary concept. It means that the entire ledger is not stored on a single central server but is distributed, copied, and stored on thousands of computers (nodes) around the world.
- Trustless System: Because no single bank, government, or person controls the data, you don't have to trust a middleman. You only have to trust the math and the collective network.
- Source of Security: If one computer storing the ledger goes down or is hacked, the network remains fully operational and secure because thousands of other copies still exist and can verify the truth.
Why Does This Matter?
Blockchain technology is more than just the engine behind cryptocurrencies; it offers three key real-world benefits:
- Immutability (Permanence): Once data is recorded, it cannot be deleted or altered. This is invaluable for legal contracts, ownership records, and secure voting systems.
- Transparency: Because the ledger is publicly distributed (though user identities are typically anonymized), transactions can be viewed by anyone, making the system inherently transparent.
- Efficiency: Transactions can be settled much faster and cheaper than traditional systems, which rely on layers of banks and intermediaries.
At its core, blockchain is just a highly secure, shared, and decentralized database. It offers a new way to record and exchange value without needing a third-party intermediary. By understanding the simple concepts of blocks, chains, and decentralization, you’ve taken the first step toward understanding the digital future.






